
Basics of FX Algo Trading: Benefits, Risks and More
“The global 2021 forex market is worth $2,409,000,000 with 79% of its share coming from the UK, USA, Hong Kong, Singapore and Japan.”
In terms of value, trading volume and liquidity, it is the largest financial market in the world as well as one that operates 24/5.
Needless to mention, the market has seen significant technological advancements in the last few decades. Digital exchange platforms that provide real-time streaming of prices have replaced traditional trading systems.
The introduction of algorithms has further transformed the nature of trading in the foreign exchange market. While algorithmic trading has offered multiple benefits to the industry, there are some inherent risks that need to be understood.
This article aims to examine the basics of FX Algo trading as well as the strengths and pitfalls of using algorithms in currency trading.
Let’s start by understanding more about Forex Markets.
Basics of the forex market
The foreign exchange (forex) market was originally created for people to trade currencies in order to buy foreign goods and services. The global forex market trades over 170 different currencies.
Currencies are often traded in pairs, and in varying volumes according to quoted prices. The most popular pairs traded are:
- US Dollar vs Euro- 24%
- US Dollar vs Japanese Yen- 17.8%
- US Dollar vs Great British Pound- 9.3%
- US Dollar vs Australian Dollar- 5.2%
- US Dollar vs Canadian Dollar- 4.3%
- US Dollar vs Chinese Yuan- 3.8%
- US Dollar vs Swiss Franc- 3.6%
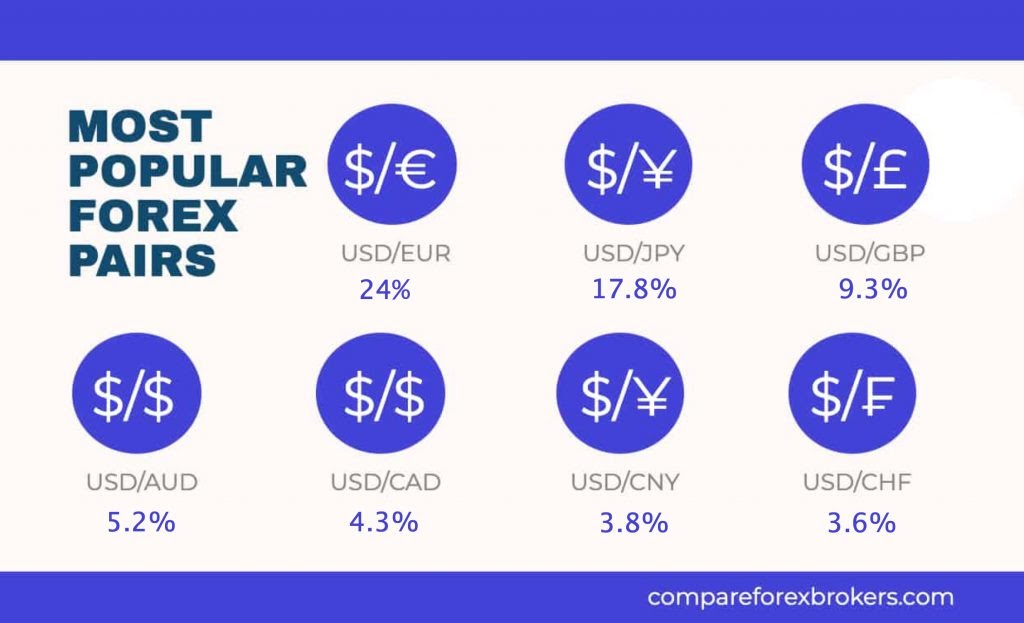
(Source: CompareForexBrokers)
Forex players include private banks, central banks, corporations, individual retail traders, large institutional investors and financial companies, such as asset management firms and brokerage firms.
What is algorithmic trading?
In layman terms, algorithmic trading is defined as trading that uses computer algorithms to perform the multiple functions needed by forex traders. It is also referred to as algo trading, automated trading, or black-box trading.
Algorithmic trading is a variation of systematic trading.
In systematic trading, traders use a quantitative algorithm to trade various assets like forex, commodities, indices and others. They utilize market signals, such as price volatility and changes in trade volume, to detect market trends early and make a profit from them.
So how do forex traders use this technology?
Specific instructions are fed into the software. These include information regarding time, price, quantity, or any other programmable attributes. The software then follows a pre-set collection of instructions and performs the desired functions.
Trades are automatically placed at the best prices, and the software is capable of following the schedule fixed by the hedge fund manager.
The software is capable of performing vast volumes of rapid transactions and calculations to determine optimal “take profit” and “stop-loss positions”.
Algo trading in the forex market
About 30 years ago, the typical scene in a forex market consisted of traders shouting into telephones. Digitisation has made it possible for trades to be executed through algorithms.
As mentioned earlier, an algorithmic trading software executes trades based on predetermined criteria without the need for human monitoring.
This automated feature of algorithms is far more efficient than traditional manual trading techniques. It has made the process faster with a capacity to trade in larger volumes every single day.
The efficiency created by automation has also led to lower costs in carrying out various forex processes such as the execution of trade orders.
Aside from the stock exchange and forex market, financial institutions such as banks have also adopted algorithms due to the advantages which they offer, though they tend to perform flow trading rather than trading for alpha.
Algorithms can auto-update the prices of currency pairs on electronic trading platforms, therefore, increasing the speed at which banks can quote market prices. Consequently, it means that the number of manual working hours it takes to quote prices is significantly reduced.
Algorithms are also being programmed by some banks to reduce risk exposure.
Take this as an example.
When an algorithm is used to maintain a fixed quantity of a particular currency sold by the bank, the software can match the correct currency to a customer’s trade, thereby reducing the risk exposure for holding that currency.
And because the processes involved are more efficient via algorithms, the cost of transaction is lowered.
The ability of algos to interpret data instantly and execute orders 24 hours a day makes high frequency trading possible. This allows traders to exploit arbitrage opportunities arising from small price deviations between currency pairs. Though such opportunities have dwindled in recent years with increasing market efficiency.
This ability is also the reason why algorithms are suitable for executing spot contracts and currency options, both being the primary methods of hedging trades in the forex market.
Different types of algo trading in forex
There are 4 basic types of algo trading in financial markets:
- Statistical analysis of historical data to look for profitable trading opportunities.
- Auto-hedging to create a set of rules that reduce risk exposure.
- Algorithmic execution strategies are defined to perform based on predefined objectives.
- Direct market access relates to the speed and costs that are used to access multiple trading platforms.
Traders who are able to execute the above can use them to implement the following with algorithms:
- Trend momentum trading
- Paired momentum trading
- Arbitrage (volatility breakouts in currency pairs)
- Forex scalping
- Straddle trading
- Range trading
Benefits of FX algo trading
The following are some key benefits associated with algorithmic trading in forex.
-
Better trade prices
The forex market is open 24 hours a day, 5 days a week. Opportunities can spring up at odd times and can be easily missed for spot contracts.
Because algorithmic trading is pre-set to execute trades automatically according to desired criteria, it can do so at any time and at a much faster pace than manual trading. This means traders using algo trading will have a much higher possibility of executing trades at their desired price, irrespective of the time of the day.
-
Saves time
Once an algorithm is set up, it can be left to work without any human supervision. This means traders can focus on other work, such as monitoring world trends and events to anticipate and prepare for future fluctuations in price.
-
Not obstructed by emotions or personal bias
Algorithms are computer programs which follow instructions. They are not influenced by human emotions or prejudices, which could cause emotional decision-making and adversely affect trading outcomes.
-
Ability to backtest strategies
Trading strategies follow a sequential rule system allowing fund managers to back-test its effectiveness. Backtesting refers to the ability to test strategies based on historical data. The fund managers can create a hypothetical situation and view the results if the strategies were executed in the past.
While backtesting is not a foolproof idea as actual trading conditions tend to vary wildly from ideal execution conditions, it gives the manager an idea of how the strategy may fare in a given scenario.
The speed with which backtesting can be done allows for quick iteration of trial strategies, rapid improvements to the original strategy, and elimination of those which do not seem feasible.
It is still required to perform “forward testing”, with real funds and connected to actual liquidity feeds for a period of time in order to obtain accurate data on actual performance of the selected strategies before considering inclusion to the actual fund.
-
Lower risk
Because algos are thoroughly tested in various scenarios and conditions before going live, the risk of heavy losses is much lower than that of manual trading.
Risks involved in FX algo trading
All trading techniques have inherent risks associated with them. The following are some discussions on risks involved in FX algo trading (based on three hypothetical situations and two possible scenarios):
-
Imbalance of market participants
The efficacy of algo trading could cause an imbalance in the trading power of market participants causing it to tip in favour of those who have the means to acquire and use algorithms.
Though not proven at this point, this imbalance could possibly create fragmentation within the market as well as liquidity shortages over time.
-
Black swan events
Some traders believe that the stock market flash crash which occurred in 2010 could happen in the forex market if high-frequency trading via algorithms is applied.
Traders have often voiced concerns that an algorithm may not be able to respond fast enough to unforeseen market changes since it is programmed only for specific market scenarios.
However, this is where the fund managers play a role.
The time freed by algorithms allows fund managers to monitor market trends and global events more thoroughly. This enables them to safeguard their clients’ investments by adjusting the algorithms before any major losses occur. Moreover, given the stringent risk requirements by institutional clients, fund managers in the FX space have a robust risk framework in place to maximize capital preservation and minimize risk.
-
Exacerbate market reactions
The risk discussed in this point is hypothetical, based on a scenario where algo trading is suspended during market turbulence. Simultaneous algorithmic trading by numerous market participants could result in high volatility and a drastic reduction in market liquidity.
-
High costs involved
For hedge funds employing systematic trading in their strategies, it is essential to ensure optimal trading execution conditions.
The cost of acquiring the right talent to come up with new strategies and maintaining them is high. Additionally, high costs are incurred in ensuring that the underlying infrastructure of the algorithm strategies is hosted close to the trading counterparties to ensure minimal slippages.
-
Self-sabotage
It is mostly applicable in cases where a trader manually overrides the system.
While there may be situations where this is necessary to avoid risks, the override may happen when a trader’s emotions result in an erroneous decision that goes against the trading strategy, resulting in losses.
Conclusion
The use of algorithms in forex trading favours traders and investors who can benefit from better outcomes and lower risk. The potential effects of risks may be seen mainly on the market and fund managers with less likely negative impacts on investors.
Investors who wish to minimise their risks should select fund managers with extensive experience in algo trading and knowhow of forex market intricacies. Another way is to participate in a fund offered by registered fund management companies regulated by reputable jurisdictions such as Singapore instead of placing their own trades in the forex market.
Salzworth Asset Management offers an investment opportunity within the Forex Market via the Salzworth Global Currency Fund – a diversified set of profitable trading systems, focusing on FX spot trading in G10 currencies, underpinned by a robust risk management framework.
Algorithmic trading is evolving because of the advancement in technology. What is relevant today may easily change in the near future, especially so as certain algorithms may work better than others in certain market conditions.
As this space continues to mature, we can expect more efficiency and innovation, which underscores the need for an experienced team of FX Algorithm traders and fund managers to select the optimal strategies for investors.
Other related articles:
- What is Systematic Trading?
- What are Algo Funds?
- Shedding Light on Foreign Currency Denominated Funds



